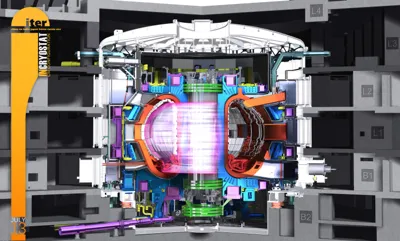
ITER: The Future of Fusion Energy
| Summary/Static | Details |
|---|---|
| Why in the news? | ITER: The Future of Fusion Energy |
| Type | Magnetic Confinement Fusion Reactor (Tokamak) |
| Location | France |
| Participating Nations | 35 (including US, China, India, EU, Japan, Korea, Russia) |
| Objective | Achieve sustainable fusion energy through burning plasma |
| Key Goal | Fusion gain (Q > 10) for 400-600 seconds |
| Plasma Temperature | 150 million °C (10 times hotter than the Sun's core) |
| Plasma Size | 6.2m plasma radius, 840m³ volume |
| Magnetic Confinement System | Central solenoid, poloidal magnets, toroidal-field coils, correction coils, cryostat |
| India's Contribution | Cryostat, cooling system, heating systems, diagnostics, shielding materials |
| India's Contribution % | 9% of total project costs |
| Significance | Future clean energy source, major breakthrough in burning plasma |