Rajasthan's River-Link Project: Environmental Concerns and Key Details
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Project Name | Parbati-Kalisindh-Chambal-Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (PKC-ERCP) |
| Objective | Address water scarcity in Rajasthan by channeling surplus water from Chambal River basin for irrigation, drinking, and industrial use. |
| Beneficiaries | 23 districts of Rajasthan, benefiting 3.45 crore people. |
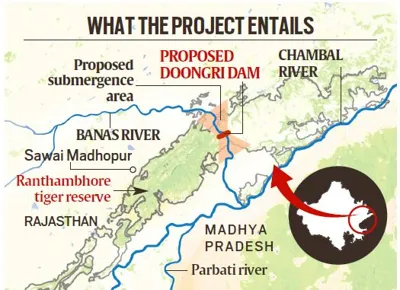
| Total Submergence Area | 408.86 sq km |
| Submergence in Banas River Dam | 227 sq km (proposed dam near Doongri village, 39 meters high, 1.6 km long). |
| Submergence in Ranthambore | 37.03 sq km (Ranthambore National Park and Keladevi Wildlife Sanctuary). |
| Tiger Population in Ranthambore | 57 tigers. |
| Other Affected Tiger Reserves | North Koel Reservoir Project (Palamu, Jharkhand): 10.07 sq km; Ken-Betwa River Link (Panna, Madhya Pradesh): 41.41 sq km. |
| Chambal River Details | Originates at Singar Chouri peak, Vindhya mountains; length: 603 km; flows through MP, Rajasthan, and UP. Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Sipra, Parbati. Dams: Gandhi Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, Jawahar Sagar, Kota Barrage. |
| National Chambal Sanctuary | Located along the Chambal River in MP, Rajasthan, and UP; home to gharial, red-crowned roof turtle, and Ganges river dolphin. |