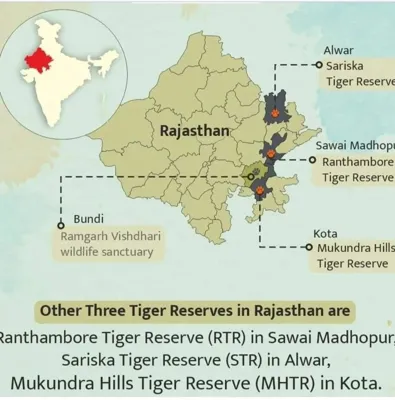
New Tiger Reserve in Rajasthan: Kumbhalgarh-Todgarh Raoli Sanctuary
| Topic | Details |
|---|---|
| Event | Proposal to declare Kumbhalgarh-Todgarh Raoli sanctuary as a Tiger Reserve. |
| Why in News? | An expert committee recommended urgent habitat conservation and prey base development before the declaration. |
| Approval | In-principle approval granted by the Union government and National Tiger Conservation Authority in August 2023. |
| Committee's Recommendations | |
| Habitat Limitations | The current area cannot support a sustainable tiger population. More areas need to be added to the reserve. |
| Village Relocation | Voluntary relocation of sparsely populated villages within the proposed reserve area is recommended for undisturbed habitats and better living conditions. |
| Invasive Species Control | Removal of invasive weeds and planting native, palatable grasses to restore habitats for wild herbivores. |
| Prey Base Development | Relocation of 1,000-2,000 spotted deer (chital) to enhance prey availability. |
| Anti-Poaching and Infrastructure | Strengthening anti-poaching measures, wireless communications, and patrol roads. |
| Geographic Scope | Kumbhalgarh Tiger Reserve will span approximately 1,397 sq km across Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pali, Ajmer, and Sirohi districts in Rajasthan. |
| About Spotted Deer (Chital) | |
| Scientific Name | Axis axis |
| Habitat | Open grasslands, savannas, and lightly forested areas in India and Sri Lanka. |
| Conservation Status | IUCN Red List: Least ConcernWildlife Protection Act, 1972: Schedule II. |