Hurricane Oscar: Impacts and Response in Cuba
| Event | Details |
|---|---|
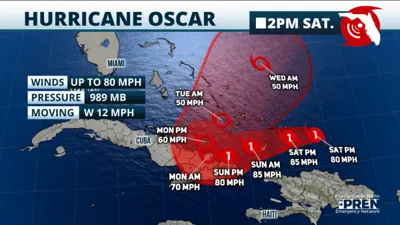
| Hurricane Oscar | Made landfall in the Bahamas, crossed Cuba's eastern coast, caused at least 6 deaths, and widespread destruction. |
| Blackouts and Protests | Prolonged blackouts began Thursday, triggering protests in urban areas like Santos Suarez and central Havana. Residents protested water shortages, food spoilage, and power outages. Government issued warnings against vandalism. |
| Energy Crisis | Cuba's energy supply struggles with only 700 megawatts available against a peak demand of 3 gigawatts. Key power plants remain down. Government blames U.S. trade embargo; U.S. attributes it to mismanagement. |
| Foreign Support | International aid offered by Mexico, Venezuela, and Russia. Crisis persists, severely affecting daily life. |
| Key Points About Hurricanes | - Definition:Tropical cyclones with winds exceeding 74 mph (119 km/h).- Categories:1 to 5 (Category 5: winds >157 mph).- Formation:Warm ocean waters (≥26°C or 79°F), June-November in the Atlantic.- Structure:Eye, eyewall, and spiral rain bands.- Impacts:Destructive winds, storm surges, heavy rainfall, and tornadoes.- Regions Affected:Atlantic Ocean, Caribbean Sea, Gulf of Mexico, Pacific Ocean.- Naming:By WMO using alphabetical lists.- Monitoring:National Hurricane Center (NHC) via satellites, aircraft, and radars.- Preparedness:Evacuations, securing properties, and emergency supplies.- Climate Impact:Rising sea temperatures may increase frequency and intensity. |