FATF Revises Grey List Criteria to Focus on High-Risk Countries and Support LDCs
| Summary/Static | Details |
|---|---|
| Why in the news? | The Financial Action Task Force (FATF) has introduced significant changes to its criteria for placing countries on its grey list. |
| Purpose of FATF | To identify jurisdictions with deficiencies in combating money laundering, terrorist financing, and proliferation financing. |
| FATF's Revised Criteria | Focuses on countries meeting specific risk criteria, prioritizing FATF Members and countries with financial sector assets above USD 10 billion. LDCs are not prioritized unless they pose significant risks. |
| Extended Observation Period for LDCs | LDCs get a longer observation period (up to 2 years) to address deficiencies and improve systems. |
| Impact of Reforms | Expected to reduce by half the number of low-capacity countries on future grey lists, focusing efforts on high-risk countries. |
| FATF Grey Listing Process | Countries with weak Anti-Money Laundering/Countering the Financing of Terrorism (AML/CFT) systems are placed on the grey list. |
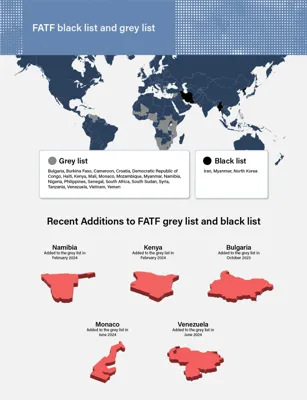
| Countries on FATF Grey List | Includes Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Haiti, Kenya, Mali, Venezuela, and others. |
| About FATF | FATF is an intergovernmental body established in 1989 to combat money laundering and terrorist financing. Headquartered in Paris. |
| FATF Members | 39 members, including the U.S., India, China, Saudi Arabia, EU, etc. India became a member in 2010. |
| Black List | Countries (NCCTs) supporting terror funding and money laundering, such as North Korea, Iran, and Myanmar. |