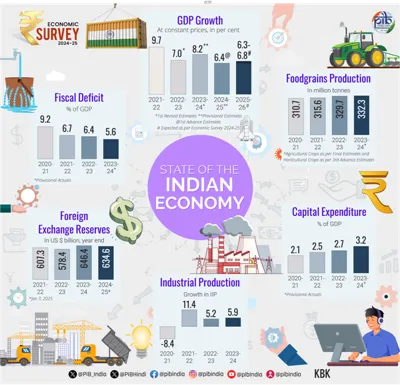
| Chapter 1: State of the Economy | - Global economy: Uneven growth, manufacturing slowdown in Europe and Asia, services sector growth. - India's GDP growth: 6.4% projected for FY25. - Agriculture and services drove growth; manufacturing struggled. - Strong external balance, fiscal discipline, and service sector trade surplus. - Food inflation may ease due to strong Kharif harvests. |
| Chapter 2: Monetary and Financial Sector Developments | - RBI held repo rate at 6.5%, later cut CRR to 4%, injecting ₹1.16 lakh crore. - Bank credit grew steadily; NPAs declined; profitability improved. - Capital market: Increased IPOs, investor participation, and financial inclusion. |
| Chapter 3: External Sector: Getting FDI Right | - Strong trade performance in FY24 despite global uncertainties. - Focus on FDI to boost manufacturing and technology. - Resilient balance of payments with services sector surplus. |
| Chapter 4: Prices and Inflation | - Global inflation: Peaked at 8.7% in 2022, declined to 5.7% in 2024. - India's retail inflation: Moderated to 4.9% in FY25. - Food inflation driven by onion and tomato production; mitigated by buffer stocking. |
| Chapter 5: Medium-Term Outlook: Deregulation Drives Growth | - India aims for 8% annual growth to become a $5 trillion economy by FY28 and $6.3 trillion by FY30. - Emphasis on regulatory reforms and ease of doing business. |
| Chapter 6: Investment and Infrastructure | - Public capex boosted infrastructure investment. - Growth in renewable energy, digital, urban, and rural infrastructure. - Continued investment needed to sustain growth. |
| Chapter 7: Industry: Business Reforms and Growth | - Strong performance in core industries (steel, cement, chemicals). - Deregulation and PLI schemes (e.g., air conditioners) boosted growth. - MSME sector saw significant growth due to policy interventions. |
| Chapter 8: Services Sector: New Challenges | - Strong performance in IT, business services, and logistics. - Steady FDI inflows into services. - Improvements in railways, airways, and waterways boosted domestic tourism. |
| Chapter 9: Agriculture and Food Management | - Agriculture growth supported by PM-KISAN and Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojna. - Challenges in pulses and oilseeds productivity. - Push for sustainable farming practices. |
| Chapter 10: Climate and Environment: Adaptation Matters | - Focus on climate adaptation and energy transition. - Lessons from global energy transitions (Europe, China). - Lifestyle for Environment (LiFE) initiative promoted. |
| Chapter 11: Social Infrastructure, Employment, and Human Development | - Improved investment in health, education, housing, and sanitation. - Rural connectivity and microfinance initiatives enhanced rural quality of life. - Emphasis on gender equality and sustainable employment growth. |
| Chapter 12: Employment and Skill Development | - Unemployment rate declined from 6% (2017-18) to 3.2% (2023-24). - Labour force participation rate (LFPR) and worker-to-population ratio improved. - Focus on reskilling, upskilling, and new-skilling for Viksit Bharat 2047. |
| Chapter 13: Labour in the AI Era: Crisis or Catalyst? | - AI's impact on labour markets: Opportunities and challenges. - Need for inclusive institutions to manage disruption. - Strategic investment in education and workforce skills for equitable growth. |