-
What are Amino Acids?
- Amino acids are the fundamental molecules that serve as the building blocks for proteins.
-
Number of Amino Acids:
- There are 20 different amino acids.
-
How Amino Acids Form Proteins:
- A protein consists of one or more chains of amino acids (called polypeptides).
- The sequence of amino acids in a protein is encoded in a gene.
-
Essential Amino Acids:
-
Cannot be made by the body and must be obtained from food.
-
The 9 essential amino acids are: Histidine, Isoleucine, Leucine, Lysine, Methionine, Phenylalanine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Valine.
-
-
Non-Essential Amino Acids:
- Can be produced by the body, even if not obtained from food. Include: Alanine, Arginine, Asparagine, Aspartic acid, Cysteine, Glutamic acid, Glutamine, Glycine, Proline, Serine, Tyrosine.
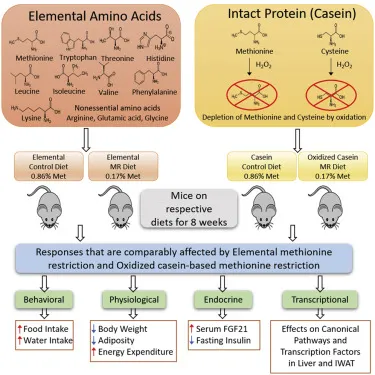
** Cysteine Restriction & Weight Loss** - "Nutrition science isn't just about adding years to life, but life to years."*
- Study: Removing cysteine from mice diets caused 30% body weight loss in 1 week.
- Mechanism: Disruption of sulfur metabolism → Impaired energy production & detoxification.
- Significance: Reveals cysteine's critical role in metabolic regulation (beyond basic nutrition).
Cysteine: Essential Facts
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Sulfur-containing, semi-essential amino acid (conditionally essential) |
| Abundance | Low in proteins but highly conserved in functional sites |
| Key Sources | Meat, eggs, dairy, legumes, whole grains |
| Biological Roles | • Collagen synthesis (skin/hair) • Precursor to glutathione (master antioxidant) • Taurine/detox pathways • Keratin (nails/skin) |
| Deficiency | Fatigue, weak immunity, stunted growth (in children) |