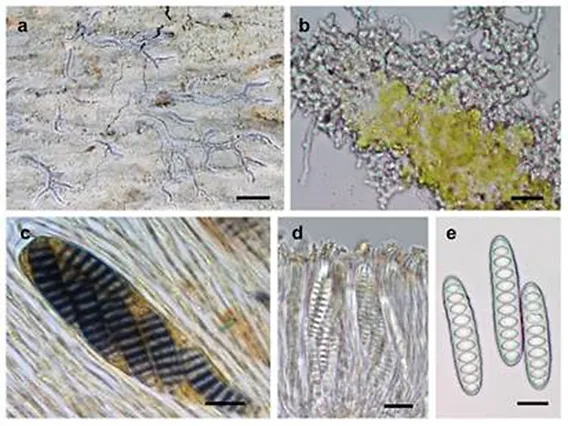
1. Key Facts: Allographa effusosoredica
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery (2023) | New lichen species found in Western Ghats (Biodiversity hotspot). |
| Type | Crustose lichen (Flat, crust-like growth). |
| Unique Features | - Effuse soredia (Powdery reproductive granules). - Norstictic acid (Rare chemical compound). |
| Research Method | Integrative taxonomy: Morphology + Chemistry (TLC) + DNA sequencing. |
| Symbiotic Partner | Photobiont: Trentepohlia (Green alga). |
| Significance | - First Allographa species sequenced from India. - Reveals local photobiont adaptation in tropics. |
| Ecological Role | Bioindicator, soil formation, microhabitat support. |
| Stats | 53rd Allographa species in India; 22nd in Western Ghats. |
2. What are Lichens?
Definition: Symbiotic association between:
- Mycobiont (Fungus, provides structure/minerals).
- Photobiont (Algae/Cyanobacteria, performs photosynthesis).
**Ecological Roles
| Role | Example |
|---|---|
| Pioneer Species | Colonize bare rocks → Initiate soil formation. |
| Bioindicators | Sensitive to air pollution (SO₂, heavy metals) → Monitor environmental health. |
| Food Source | Reindeer moss (Arctic), insects, snails. |
| Carbon/Nitrogen Fixation | Cyanobacterial lichens (e.g., Nostoc) enrich soil. |
| Habitat Creation | Support micro-arthropods (mites, springtails). |
Types of Lichens:
- Crustose (Embedded in substrate, e.g., A. effusosoredica).
- Foliose (Leaf-like, e.g., Parmotrema).
- Fruticose (Shrub-like, e.g., Usnea).